U.S. Pregnancy-Related Deaths: Alarming Trends and Solutions
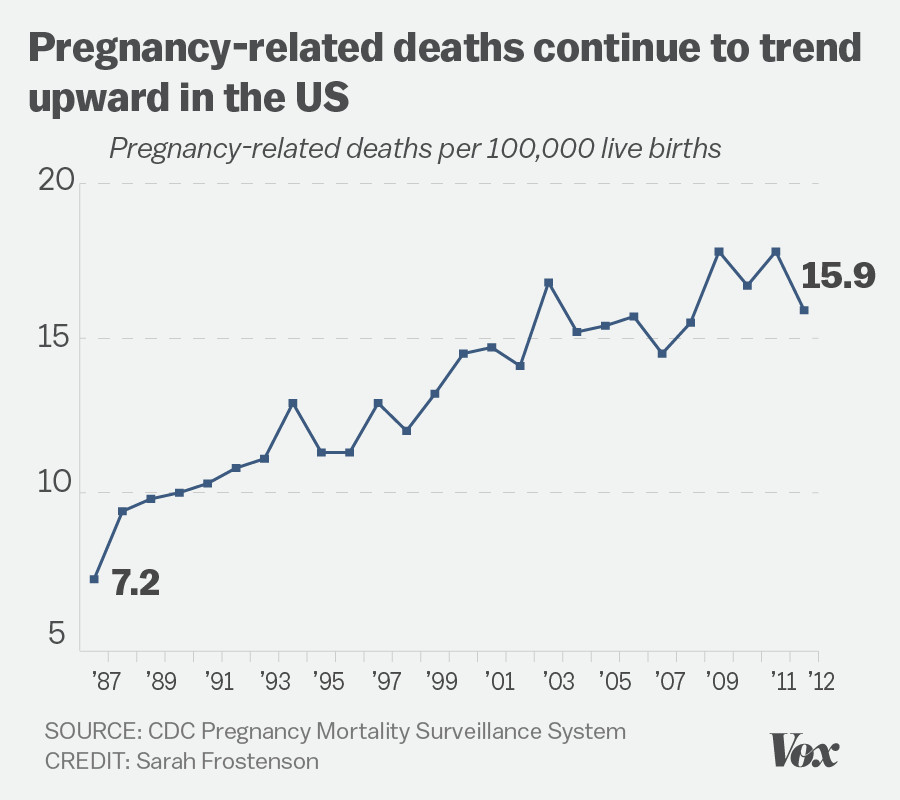
In recent years, U.S. pregnancy-related deaths have emerged as a critical public health crisis, alarming researchers and healthcare professionals alike. The United States, leading high-income nations in maternal mortality, faces an increasing trend of these preventable deaths, with more than 80% attributed to modifiable factors. Between 2018 and 2022, the rate of pregnancy-related deaths surged, exacerbated by disparities influenced by race and healthcare access. Observations show that American Indian and Alaska Native women are particularly affected, suffering mortality rates nearly four times higher than their white counterparts. This stark reality calls for enhanced pregnancy care and comprehensive postpartum health initiatives, addressing both the systemic healthcare disparities and the need for effective interventions against this troubling upward trend.
The alarming rise in maternal deaths in the U.S. highlights a growing public health concern surrounding pregnancy outcomes and maternal health. Often referred to as maternal mortality, this issue encompasses deaths related to complications from pregnancy and delivery, as well as challenges faced during the postpartum phase. A significant portion of these fatalities are preventable, revealing a troubling inefficiency in our healthcare system regarding maternity care. Furthermore, this crisis extends beyond just the statistical rise, underlining profound healthcare disparities that disproportionately affect marginalized communities. Addressing this urgent matter requires a comprehensive approach to improve healthcare access, equity, and quality throughout all stages of pregnancy and postpartum recovery.
Understanding the Rise of U.S. Pregnancy-Related Deaths
The rise in U.S. pregnancy-related deaths is a troubling trend that has placed the nation at the forefront of maternal mortality rates among high-income countries. As highlighted in recent studies, more than 80 percent of these deaths are preventable. This stark statistic underscores the urgent need for better prenatal care and postpartum health services, as well as addressing healthcare disparities that disproportionately affect marginalized communities. The correlation between rising rates of chronic illnesses, such as hypertension and cardiovascular disease, among pregnant individuals further complicates the landscape, necessitating a comprehensive examination of maternal health care policies and practices.
Moreover, the data shows that racial disparities play a significant role in the proliferation of these deaths. For instance, American Indian and Alaska Native women show a mortality rate nearly four times that of their white counterparts. Such alarming figures speak volumes about the systemic biases entrenched within the healthcare system. Creating a more equitable maternal health care framework is essential in addressing these preventable deaths, emphasizing the importance of tailored interventions that cater to the unique needs of diverse populations.
Preventable Deaths: An Urgent Call for Healthcare Reform
The alarming number of pregnancy-related deaths classified as preventable calls for immediate healthcare reform. Despite the advancements in medicine and patient care, the systemic flaws within the U.S. healthcare system lead to unnecessary loss of life. Preventable deaths are often attributed to inadequate access to quality healthcare, a lack of education about pregnancy care, and insufficient support during the postpartum recovery period. The focus must shift towards continuous and comprehensive prenatal and postpartum care, ensuring that all pregnant individuals receive the attention and resources necessary to address any health complications.
Additionally, the informal patchwork of healthcare across states creates vast discrepancies in maternal health outcomes. For example, a study noted that if all states achieved the maternal mortality rate of California, nearly 2,700 pregnancy-related deaths could have been prevented. This discrepancy emphasizes the need for nationwide policies that standardize pregnancy care, promote awareness of maternal health issues, and ensure a steady stream of funding towards research and public health initiatives focused on reducing maternal mortality rates.
The Impact of Postpartum Health on Maternal Mortality
The postpartum period is critical in determining the long-term health outcomes of new mothers. Unfortunately, many healthcare systems follow outdated models that neglect the importance of extended postpartum care, considering recovery only up to six weeks after birth. Recent findings indicate that nearly a third of maternal deaths occur after the initial postpartum period, highlighting the necessity of holistic healthcare that extends for at least one year following delivery. Addressing this gap is essential in not only preventing deaths but also in promoting overall maternal well-being.
Incorporating comprehensive postpartum care into standard practice can significantly reduce late maternal deaths. A focus on continuous monitoring and care helps identify any complications arising from childbirth, allowing for timely medical intervention. Strengthening the postpartum healthcare framework also serves to educate new mothers about the signs of complications, thus empowering them to seek help promptly. Such measures could ultimately lead to a decrease in these preventable deaths and improve the health of mothers across the nation.
Healthcare Disparities in Maternal Health and Their Consequences
Healthcare disparities are a critical factor contributing to rising maternal mortality rates in the U.S. Various socio-economic factors, including access to quality care, insurance coverage, and cultural competence in healthcare services, play a crucial role in the differences observed among various racial and ethnic groups. For instance, non-Hispanic Black women experience significantly higher pregnancy-related deaths compared to their white counterparts, indicating systemic inequities that must be addressed. Addressing these disparities through targeted policies and health initiatives can not only improve maternal health outcomes but also contribute to building trust within marginalized communities.
The consequences of ignoring healthcare disparities extend beyond individual health outcomes; they reflect broader social injustices that impact entire communities. Establishing programs aimed at reducing barriers to quality care, such as transportation assistance for prenatal visits, language services, and educational initiatives about maternal health, can bridge gaps in care and ensure that all pregnant individuals receive the support they need. By focusing on eliminating these disparities, we can move closer to achieving better health outcomes for mothers and their infants.
Policy Changes Needed to Address Maternal Mortality
To combat the rising rates of U.S. pregnancy-related deaths, it is imperative that policymakers prioritize maternal health in their agendas. This involves a commitment to not only increasing funding for maternal health research but also investing in programs that improve access to comprehensive prenatal care and extended postpartum services. Legislation aimed at reducing healthcare costs for expectant mothers and enhancing the quality of care available can have a profound impact on maternal mortality rates. Advocacy for public health initiatives that focus on preventative care and support for vulnerable populations is essential.
Furthermore, there is a pressing need for policies that actively address systemic biases in healthcare. Implementing cultural competence training for healthcare providers can help mitigate the effects of discrimination and improve the quality of care received by women of color. Additionally, collecting and analyzing data related to maternal health outcomes based on race and socio-economic status can provide the insights necessary for targeted interventions. By fostering an inclusive approach to maternal health policy, we can work towards a future where all mothers have the opportunity to thrive.
The Role of Chronic Conditions in Maternal Mortality Rates
Chronic health conditions contribute significantly to rising maternal mortality rates, with cardiovascular diseases emerging as a leading cause. Conditions such as hypertension and diabetes can complicate pregnancies and increase the risk of adverse outcomes for both mother and baby. The shift in focus from obstetric complications like hemorrhage to chronic illnesses underscores the need for awareness and proactive management of women’s health prior to conception as well as throughout pregnancy. Ensuring that women of reproductive age have access to preventive healthcare can help mitigate these risks.
Additionally, healthcare providers must be vigilant in monitoring chronic conditions during pregnancy. Regular assessments and tailored treatment plans can help manage these underlying issues and prevent complications. By fostering a healthcare environment that emphasizes the importance of managing chronic conditions, practitioners can play a pivotal role in reducing pregnancy-related deaths and ensuring healthier outcomes for mothers and their children.
The Importance of Tracking Maternal Deaths for Better Outcomes
Accurate tracking and reporting of maternal deaths are essential for understanding the complexities of maternal mortality in the U.S. The implementation of the pregnancy checkbox on death certificates has provided researchers with better data since 2018, allowing for a more comprehensive analysis of causes and contributing factors. This information is crucial for identifying trends and areas requiring intervention and for formulating policies aimed at reducing pregnancy-related deaths overall. Continual improvements in data collection methods will ensure a more detailed and accurate understanding of maternal health.
A focused effort on tracking maternal deaths can lead to insights that drive effective public health initiatives. For example, examining the reasons behind deaths occurring in specific demographics can highlight healthcare disparities and systemic flaws that require urgent attention. By consistently measuring and analyzing maternal health outcomes, stakeholders can adapt strategies in real-time, leading to improved healthcare policies and interventions that could ultimately save lives and enhance postpartum health.
Innovative Solutions for Enhancing Maternal Care
In light of the rising maternal mortality rates, there is an urgent need for innovative solutions to enhance pregnancy care. Among these solutions is the integration of telehealth services, which can provide accessible medical consultations for expectant mothers, especially in underserved areas. By leveraging technology, healthcare providers can offer valuable guidance during prenatal and postpartum periods, ensuring that women receive timely interventions and support regardless of their location. This approach can be especially beneficial in rural communities with limited access to healthcare facilities.
Additionally, creating community-based support programs can play a crucial role in improving maternal health outcomes. Such programs can foster connections among mothers, provide educational resources, and ensure that women feel supported throughout their pregnancy and the postpartum journey. By establishing networks that incorporate both medical assistance and emotional support, we can empower women and help them navigate the challenges of pregnancy more effectively, ultimately leading to decreased rates of preventable deaths.
Advocating for Comprehensive Maternal Health Frameworks
Advocating for comprehensive maternal health frameworks is vital to addressing the alarming rise of pregnancy-related deaths. By prioritizing policy changes that focus on preventive care and equitable access to healthcare, stakeholders can make strides toward reversing troubling trends in maternal mortality. Efforts to enhance the quality of care during not only pregnancy but also the extended postpartum period are essential. Such frameworks should incorporate continuous education for healthcare providers and strengthen the social support systems that women need during this critical time.
Moreover, public awareness campaigns can shed light on maternal mortality issues and encourage community involvement in maternal health advocacy. Engaging stakeholders, including healthcare providers, policymakers, and community members, can foster a unified approach toward creating sustainable changes in the maternal health landscape. Through collective efforts and a commitment to elevating maternal health standards, we can work towards a future where all mothers have access to the care they need, resulting in healthier families and stronger communities.
Frequently Asked Questions
What are the key factors contributing to U.S. pregnancy-related deaths being higher than in other high-income countries?
The key factors contributing to higher U.S. pregnancy-related deaths include a fragmented healthcare system, inequitable policies, the prevalence of maternity care deserts, and ongoing biases affecting racial and ethnic groups. Additionally, an increase in chronic health conditions among reproductive-age individuals also plays a role in elevated maternal mortality rates. Understanding these factors is crucial for developing effective interventions in pregnancy care.
How do healthcare disparities impact maternal mortality rates in the U.S.?
Healthcare disparities significantly impact maternal mortality rates in the U.S. There are marked differences in pregnancy-related death rates by state, race, and ethnicity, with groups such as American Indian and Alaska Native women experiencing disproportionately high mortality. Addressing these disparities through policy reforms and equity-focused healthcare initiatives is essential to reduce preventable deaths during pregnancy and the postpartum period.
What are the leading causes of pregnancy-related deaths in the U.S. and how have they changed over time?
Cardiovascular disease is currently the leading cause of pregnancy-related deaths in the U.S., accounting for over 20% of fatalities. This marks a shift from previous decades where complications like hemorrhage were more common. The increase in chronic conditions such as hypertension among younger women has contributed to this trend, indicating a need for improved pregnancy care and health management throughout the perinatal period.
Why is it important to include late maternal deaths in discussions about pregnancy-related mortality?
Including late maternal deaths—defined as deaths occurring between 42 days and one year postpartum—in discussions about pregnancy-related mortality is vital because this timeframe reflects ongoing health risks that women face after childbirth. Acknowledging and addressing these deaths can lead to more comprehensive postpartum health care and improve overall maternal health outcomes, as many deaths are preventable with appropriate care.
What potential solutions can help reduce U.S. pregnancy-related deaths?
To reduce pregnancy-related deaths in the U.S., there must be a renewed investment in public health infrastructure, particularly targeting quality of care during pregnancy and the postpartum period. Innovative solutions, such as better tracking of maternal health data, addressing healthcare disparities, and implementing successful state-level practices, are essential for improving outcomes and ensuring equitable access to comprehensive pregnancy care.
How can community and state policies be improved to address the rising rates of pregnancy-related deaths?
Improving community and state policies to address rising pregnancy-related deaths involves understanding the factors behind state-level disparities and implementing tailored interventions. This includes enhancing access to quality healthcare, securing funding for maternal health programs, and promoting policies that prioritize maternal health equity. Collaboration between healthcare providers, policymakers, and community organizations is crucial to effect meaningful change.
What role does the postpartum period play in maternal health and mortality?
The postpartum period is critical in maternal health and mortality, as it is a time when women may experience significant health issues that are often overlooked. Studies show that a substantial number of pregnancy-related deaths occur in the months following childbirth. Recognizing postpartum health as a continuum rather than a definitive end-point is essential for providing adequate care and reducing the number of preventable deaths.
What impact did the COVID-19 pandemic have on U.S. pregnancy-related mortality rates?
The COVID-19 pandemic had a notable impact on U.S. pregnancy-related mortality rates, especially highlighted by a sharp increase in deaths in 2021. The pandemic strained healthcare resources, and pre-existing health disparities were exacerbated, leading to higher mortality rates among vulnerable populations. Continued study of these implications is essential for improving maternal health responses in future public health emergencies.
| Key Point | Details |
|---|---|
| U.S. pregnancy-related deaths on the rise | The U.S. has the highest maternal mortality rate among high-income countries, with a rising trend from 2018 to 2022. |
| Preventable deaths | More than 80% of pregnancy-related deaths could have been prevented with better care. |
| Disparities by race and state | Significant disparities exist with American Indian and Alaska Native women facing the highest rates of maternal mortality. |
| Cardiovascular disease as leading cause | Cardiovascular conditions are now the leading cause of pregnancy-related deaths, accounting for over 20%. |
| Increase across age demographics | Pregnancy-related deaths increased for all age groups between 2018 and 2022. |
| Importance of extended postpartum care | Late maternal deaths (deaths up to 1 year postpartum) account for nearly 1/3 of total deaths. |
| Need for public health investment | Investment in public health and maternal care is crucial to reduce pregnancy-related deaths. |
Summary
U.S. pregnancy-related deaths have become a critical public health issue, reflecting systemic healthcare challenges that need urgent attention. The alarming trends highlight the need for targeted interventions to reduce preventable deaths, address racial disparities, and improve maternal care across the country. Investing in better healthcare systems, especially during the postpartum period, is essential in altering the trajectory of maternal mortality rates in the U.S.