Genetic disorders treatable before birth represent a groundbreaking frontier in prenatal medicine, offering hope to families facing serious genetic conditions. Recent advancements in prenatal genetic testing have revealed nearly 300 genetic disorders that can now be addressed during pregnancy or shortly after birth. With the power of early intervention genetics, medical professionals can provide timely treatments that significantly improve outcomes for affected fetuses. Techniques such as fetal therapy and genomic sequencing prenatal are paving the way for effective management of treatable genetic conditions, bridging critical gaps in prenatal care. As researchers continue to explore these possibilities, the landscape of prenatal diagnostics and treatment is evolving rapidly, making early detection more vital than ever.
The realm of in-utero genetic therapy is revolutionizing how expectant parents prepare for potential health issues in their unborn children. With advancements in prenatal diagnostics, conditions that were once thought untreatable are now being redefined through innovative methods of early intervention. This emerging field not only encompasses prenatal genetic testing but also includes the latest strategies in fetal therapies, allowing for actionable insights into treatable fetal abnormalities. Additionally, genomic sequencing plays a crucial role in identifying genetic predispositions before birth, significantly altering the trajectory of care following delivery. As our understanding of genetic conditions expands, so too does the opportunity for informed decision-making for families, empowering them with options for managing health even before the arrival of their child.
Understanding Treatable Genetic Disorders Before Birth
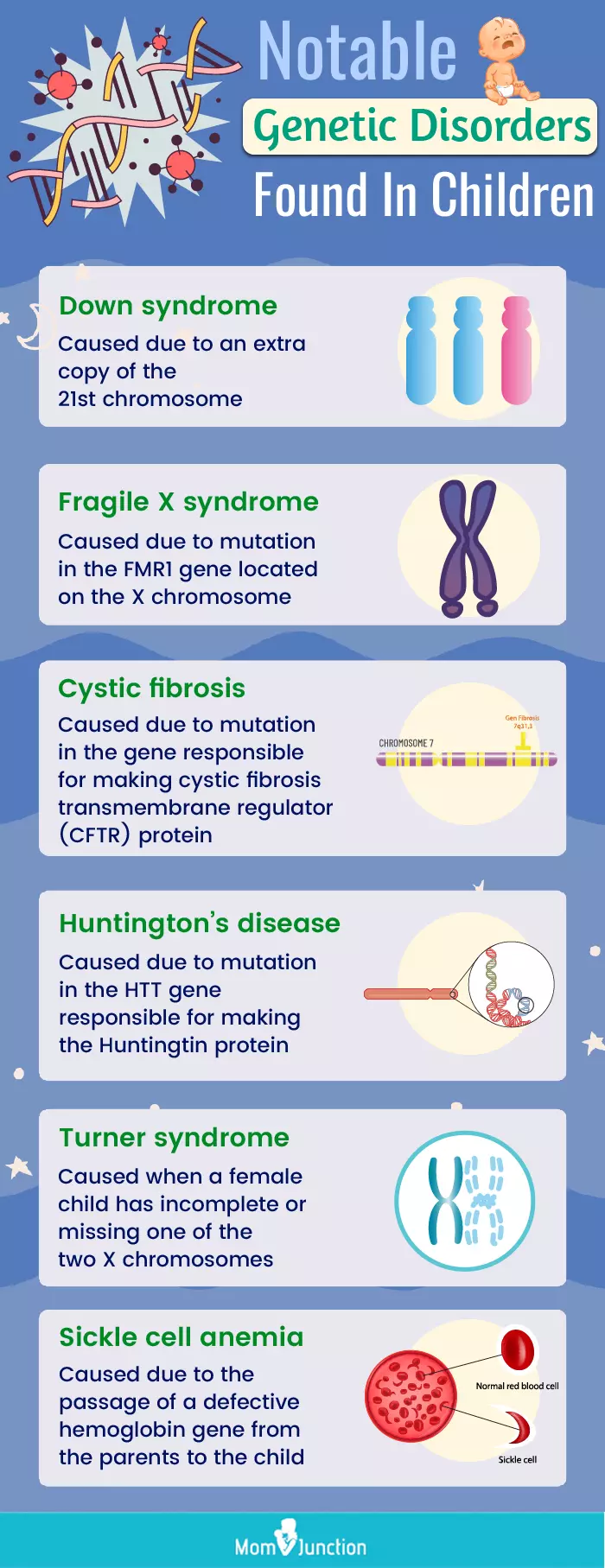
The recent advancements in prenatal genetic testing allow for the identification of genetic disorders that can be treated even before birth. Researchers have compiled a significant list of 296 genetic conditions that can be detected during pregnancy or within the immediate period after birth, known as the ‘treatable fetal findings list.’ This list reveals that many genetic conditions, once considered irreversible, can actually be managed with early intervention. Timely diagnosis through prenatal techniques like genomic sequencing enhances the options parents have and can significantly improve health outcomes for the unborn child.
Innovative approaches in fetal therapy represent a remarkable leap in medicine, creating pathways to treat conditions such as congenital heart defects or metabolic disorders while the baby is still in utero. By employing targeted prenatal therapies and interventions, healthcare professionals can proactively address potential health issues, reducing long-term morbidity and mortality. This proactive method allows for a comprehensive care strategy that can empower families and provide them with critical knowledge for making informed health decisions.
The Role of Genomic Sequencing in Prenatal Care
Genomic sequencing has revolutionized prenatal diagnoses and has become an essential tool for identifying genetic abnormalities that may affect fetal development. It allows medical professionals to pinpoint specific genes responsible for detected issues during routine ultrasound scans. With genomic data, clinicians can assess the risks of treatable genetic conditions before birth, offering families the opportunity to plan for necessary interventions right after delivery or, in some cases, throughout the pregnancy.
Furthermore, this technology serves as an invaluable resource by uncovering not only expected genetic disorders but also incidental findings that could signify predisposition to serious health conditions. Conditions that can be managed, such as gastrointestinal disorders or hormonal deficiencies, can be effectively treated with simple interventions, medications, or therapies based on genetic information. Thus, by integrating genomic sequencing into standard prenatal care, parents are presented with the necessary tools to ensure the best possible health outcomes for their child.
Challenges and Ethical Considerations in Early Intervention Genetics
Despite the promising prospects of treating genetic disorders before birth, there are several challenges and ethical considerations to navigate. The influx of complex genetic information can be overwhelming for expectant parents, many of whom may face uncertainty about the implications of findings from prenatal genetic testing. It is crucial for healthcare professionals, including genetic counselors and obstetricians, to provide clear, contextual information to help families understand their options and the potential outcomes associated with early intervention.
Additionally, the ethical dimension of such interventions is significant, as expectant parents must grapple with decisions affecting their child’s future health. Questions around consent, the psychological impact of knowing potential health issues, and the pressure of making medical decisions lay heavily on families. As emphasized by researchers, a collaborative approach among healthcare providers is vital in guiding families through this intricate landscape of prenatal care, ensuring that they receive not just information, but also the support required to navigate these life-changing choices.
The Importance of Early Intervention in Genetic Disorders
Early intervention is critical when it comes to managing genetic disorders. The earlier that conditions are identified, the better the chances of effective treatment, which can lead to improved outcomes and quality of life for affected individuals. Research demonstrates that treating conditions such as metabolic disorders or congenital abnormalities early on can prevent irreversible damage and enhance the efficacy of therapies. By empowering parents with knowledge of their unborn child’s health, they can make proactive decisions that change the trajectory of their child’s developmental journey.
Moreover, the initiative to compile a list of treatable conditions aims to broaden the scope of prenatal care, offering families choices they previously did not have. With advancements such as fetal surgeries or immediate postnatal interventions, parents can embark on a path toward better management options. This expands not only medical possibilities but also provides psychological reassurance to families, allowing them to approach parenthood with a sense of agency and optimism.
Navigating Information Overload in Prenatal Genetic Testing
As we delve into the landscape of prenatal genetic testing, one of the foremost challenges is the sheer volume of information that can be overwhelming for prospective parents. Many families may not have experience navigating complex genetic data, and the potential implications of test results can lead to anxiety and confusion. It is essential for healthcare providers to simplify this process and ensure that expectant parents receive clear and concise information alongside expert guidance.
In this context, a structured approach to sharing information is vital. Programs that incorporate educational resources, support groups, and clear communication strategies can help families better understand their options regarding treatable genetic conditions. By fostering an environment of trust and understanding, healthcare teams can engage parents meaningfully in their child’s prenatal care, ultimately making the journey more manageable and informative rather than overwhelming.
Genomic Sequencing: Unlocking New Treatment Avenues
Genomic sequencing stands at the forefront of modern prenatal genetic testing, unlocking new avenues for treatment options that were previously unreachable. This sophisticated technology helps identify not only genetic disorders that are present but also potential health concerns that may emerge later. By catching these issues early, expecting parents can explore available interventions — whether they be surgical options or medication therapies — that enhance fetal wellbeing and prepare them for any postnatal care that may be needed.
The potential of genomic sequencing goes beyond just detection; it serves as a critical pathway for strategic interventions that can mitigate risks associated with specific genetic conditions. By outlining potential treatment plans based on the genetic profile of the fetus, parents can collaborate with healthcare providers to make informed decisions regarding their pregnancy and childbirth, ultimately fostering a proactive approach to health management from the very beginning.
A Comprehensive Approach to Prenatal Care
The integration of genetic testing and early intervention practices into prenatal care represents a comprehensive approach to maternal and fetal health. This new paradigm shifts the focus from reactive care after birth to proactive strategies during pregnancy. As research continues to identify additional treatable conditions, it becomes increasingly important for healthcare systems to adapt and prioritize multifaceted care that includes genetic counseling, extensive diagnostic testing, and informed decision-making.
Moving forward, it is crucial to enrich the prenatal care framework with continuous education for both healthcare providers and parents. By doing so, we can cultivate an environment that promotes the understanding of risks and benefits associated with genetic disorders that are treatable before birth. This comprehensive methodology will not only empower families but enhance the overall quality of prenatal healthcare.
Training Healthcare Professionals in Prenatal Genetic Care
As advances in prenatal genetic testing continue to unfold, there is a pressing need to train healthcare professionals to effectively manage the complexities associated with the emergence of treatable conditions. The collaboration between obstetricians, medical geneticists, and genetic counselors is vital to ensure that expectant parents receive the best information and care possible. Workshops and further education will enable these professionals to communicate complicated genetic information clearly and empathetically.
Moreover, integrating interdisciplinary training programs can foster teamwork and establish protocols for the management of prenatal care effectively. By emphasizing joint efforts among various healthcare specialists, we cultivate an efficient system capable of navigating the nuances of genetic disorders and administering appropriate interventions that can significantly improve outcomes for families. Building this foundation of expertise can ultimately transform the landscape of prenatal genetic practice.
The Future of Prenatal Genetic Testing and Treatment
Looking toward the future, the field of prenatal genetic testing and treatment is poised for significant evolution. As technology advances, we are likely to see further developments in non-invasive testing methods that make detection more accessible and safer for both mothers and babies. Future studies may expand on the current 296 treatable genetic conditions, broadening the horizons for intervention and improving the overall health landscape for families.
Additionally, as awareness about the potential of early intervention genes grows, public expectations around prenatal care will shift. The inclusion of genetic counseling as a standard part of prenatal care will emphasize the importance of informed decision-making for expectant parents. Advanced research and innovation will continue to drive these changes, ultimately leading to improved strategies that enhance maternal and fetal health outcomes, ensuring that genetic disorders treatable before birth become a focus of standard practice.
Frequently Asked Questions
What are genetic disorders treatable before birth?
Genetic disorders treatable before birth refer to conditions identified during prenatal care that can be addressed either during pregnancy through non-invasive procedures or immediately after birth. These include disorders where early intervention can significantly improve health outcomes for the fetus or newborn.
How does prenatal genetic testing help in treating genetic disorders before birth?
Prenatal genetic testing allows for the identification of genetic disorders in the fetus through methods such as genomic sequencing. When these conditions are detected early, healthcare providers can discuss applicable fetal therapies or postnatal treatments that can alleviate the potential impacts of such disorders.
What is the significance of early intervention genetics in managing fetal conditions?
Early intervention genetics aims to identify genetic disorders promptly, enhancing treatment options. By diagnosing conditions early in pregnancy, healthcare providers can implement fetal therapy or prepare for immediate postnatal care, improving overall outcomes and reducing risks of morbidity.
Can you explain what fetal therapy is in the context of genetic disorders?
Fetal therapy refers to medical interventions designed to treat genetic disorders in the fetus during pregnancy. This can include procedures to correct structural abnormalities or administer medication, ultimately aiming to mitigate complications before the baby is born.
What conditions are included in the ‘treatable fetal findings list’?
The ‘treatable fetal findings list’ includes nearly 300 genetic disorders identified by researchers that can be acted upon before or shortly after birth. These can range from conditions that can be treated with medication during pregnancy to those requiring immediate medical attention after delivery.
What role does genomic sequencing prenatal testing play in identifying treatable genetic conditions?
Genomic sequencing prenatal testing plays a crucial role by analyzing the fetal genome to identify genetic variations that may lead to treatable conditions. This advanced screening method allows for early detection of issues that may affect the fetus, enabling timely medical interventions.
What are some challenges faced in implementing fetal therapies for genetic disorders?
Challenges in implementing fetal therapies for genetic disorders include ethical considerations, the overwhelming nature of the information for patients, and the need for coordination among healthcare providers to effectively manage communication and treatment plans.
How can families benefit from knowing about genetic disorders treatable before birth?
Families can benefit significantly by being informed about genetic disorders treatable before birth, as this knowledge empowers them to make proactive decisions regarding prenatal care and to explore available treatment options, ultimately enhancing their child’s health outcomes.
| Key Points | Details |
|---|---|
| Research Findings | Identified nearly 300 genetic disorders treatable during pregnancy or shortly after birth. |
| Collaboration | Conducted by researchers from Harvard Medical School, Mass General Brigham, and Duke University. |
| Importance of Timely Detection | Early intervention can significantly reduce morbidity and mortality rates. |
| Role of Genomic Sequencing | A key tool in prenatal diagnosis that helps identify genetic disorders through family history and testing. |
| Ethical Considerations | Challenges exist regarding the overwhelming information for patients and the need for expert guidance. |
| Goals of the Study | To provide a list of treatable conditions and enhance options for patients during pregnancy. |
Summary
Genetic disorders treatable before birth represent a significant advancement in prenatal healthcare, allowing for timely intervention that can greatly improve outcomes for affected fetuses. A recent study identified nearly 300 genetic conditions that can now be diagnosed and treated either during pregnancy or shortly after birth. This groundbreaking research underscores the potential of genomic sequencing to revolutionize prenatal diagnostics and highlights the importance of providing expectant families with this critical information. However, the initiative also faces ethical challenges, necessitating careful navigation to ensure families receive support and clarity. Overall, these developments pave the way for enhanced prenatal care and improved quality of life for future generations.