Is sugar addictive? This question often arises as more people become aware of their sugar consumption and its implications on health. Research indicates that sugar can trigger cravings similar to those caused by addictive substances, leading many to wonder about the health effects of sugar in their diets. Regular intake of processed foods laden with added sugars not only enhances these cravings but also contributes to a cycle of overconsumption. Understanding whether sugar should be classified alongside other addictive substances is critical, as it informs our eating habits and choices.
When discussing the potential addictiveness of sugar, it’s essential to recognize it as a common ingredient in many modern diets that may provoke substantial cravings. This topic shares common ground with terms like sweeteners, sugary foods, and palatable snacks, reinforcing the dialogue surrounding our diet’s impact on health. The addictive nature of certain food items has implications for sugar intake and subsequent health consequences, especially given the prevalence of processed items in grocery stores. Diving into how these sweet substances affect our brain and behavior can provide insights into managing our cravings effectively. As we explore this subject, we might consider not only the enjoyment derived from sweetness but also the necessity of moderation and awareness in our consumption patterns.
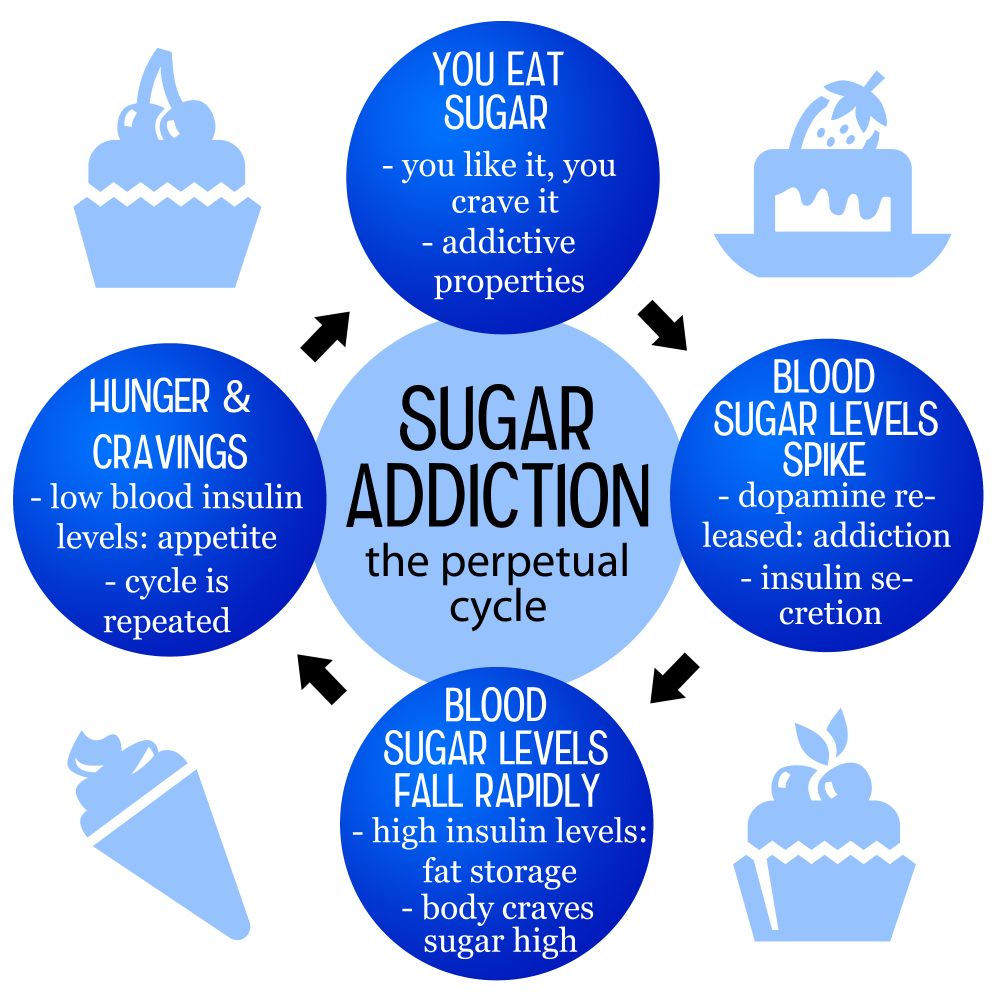
Understanding Sugar Addiction
When discussing whether sugar is addictive, it’s essential to differentiate it from other addictive substances like alcohol and nicotine. While sugar can elicit cravings and lead to compulsive eating, it fails to meet the strict clinical criteria for addiction. Nutrition experts, including Frank Hu from Harvard, argue that sugar influences our brains and bodies in ways that can mimic addiction. People often experience withdrawal-like symptoms when they cut sugar from their diets, such as headaches and anxiety. However, these symptoms are generally less severe than those associated with drugs or alcohol.
Research shows that excessive sugar intake can lead to health complications, including obesity and diabetes. Despite its pleasant taste and the happiness it can bring, too much sugar, particularly in processed foods, can heighten cravings due to its high palatability. Therefore, while sugar does stimulate the brain similarly to addictive substances, moderating its consumption is vital in maintaining a balanced diet and preventing unnecessary health risks.
The Implications of Sugar Consumption on Health
The health effects of sugar are far-reaching, especially considering the typical American consumes nearly 20 teaspoons of added sugar daily. Such high levels of sugar consumption are linked to numerous health issues, including heart disease, metabolic syndrome, and tooth decay. Understanding the impact of sugar-filled processed foods is crucial for making healthier choices. It’s also essential for consumers to be aware of hidden sugars in products that may not taste sweet, which can contribute to excessive intake without them realizing it.
Incorporating guidelines from health bodies like the American Heart Association can help mitigate the health effects of sugar. They recommend limiting added sugar intake to about 9 teaspoons for men and 6 teaspoons for women. One effective strategy is to gradually reduce sugar consumption rather than eliminating it cold turkey, as this can lead to setbacks. Small adjustments, such as reading nutrition labels and opting for whole foods over processed ones, can significantly affect overall sugar consumption and health.
The Role of Processed Foods in Sugar Cravings
Processed foods are notorious for containing high levels of added sugar, unhealthy fats, and sodium, which not only enhance cravings but also contribute to habitual overconsumption. These foods are designed to be hyper-palatable, making it easy to eat more while not recognizing how much sugar you are actually consuming. This repeated exposure leads to conditioned responses where the brain seeks the instant gratification that sugary foods provide, contributing to the cycle of cravings.
Breaking the cycle of cravings induced by processed foods requires conscious effort. Instead of reaching for sugary snacks, consider alternatives rich in nutrients that provide longer-lasting energy without spikes in blood sugar. Foods like fruits, vegetables, and whole grains satisfy hunger and help diminish sugar cravings over time, making it easier to maintain a healthier diet. Being mindful of what you eat can significantly alter your relationship with sugar and reduce dependence on processed foods.
Addressing Sugar Cravings Effectively
Sugar cravings can be challenging to manage, especially given the prevalence of sugar in processed foods. To tackle these cravings effectively, experts suggest several methods, including mindful eating practices and increasing protein and fiber intake. These adjustments can help keep you full for longer periods, thus reducing the desire for quick sugary fixes. Moreover, understanding the triggers for cravings, such as stress or lack of sleep, can lead to better management strategies.
In addition, gradual reduction in sugar can be more effective than an abrupt halt. By replacing sugary snacks with healthier options over time, cravings can diminish as the body adjusts to a lower intake of sugar. Such changes promote not only physical health but can also improve mental well-being, as one moves towards a more balanced eating pattern that includes natural sugars from fruits and vegetables.
Distinguishing Between Natural and Added Sugars
It’s vital to make a clear distinction between natural and added sugars. Natural sugars found in fruits, vegetables, and dairy come with essential nutrients that the body needs. These foods not only provide energy but also contribute to overall health and wellness. In contrast, added sugars found in many processed foods provide empty calories, leading to numerous health problems without nourishing the body.
By focusing on consuming natural sugars and minimizing the intake of added sugars, individuals can enjoy the sweetness in their diets while maintaining their health. This strategy may also help curb sugar cravings more effectively because whole foods often contain fiber, which slows down the absorption of sugar and promotes satiety. Hence, the right choices can play a significant role in regulating sugar consumption.
Hiding in Plain Sight: The Sugars in Your Daily Diet
Many consumers are unaware of the hidden sugars that lurk in everyday food items, even those that aren’t considered sweet. From sauces to bread, sugar is often incorporated to enhance flavor and preserve freshness. This hidden consumption can significantly contribute to our overall sugar intake, making it crucial for individuals to become vigilant about reading food labels.
Understanding ingredient lists and recognizing terms used for sugar can help distinguish healthier options from those laden with hidden sugars. By choosing minimally processed products and cooking more meals at home, it’s possible to regain control over your sugar intake and reduce the risk of health complications associated with excessive sugar consumption.
The Psychological Effects of Reducing Sugar
Reducing sugar intake can have significant psychological effects, leading to improved mood and mental clarity. Many users report feeling more energetic and less moody when they lower their sugar consumption. This improvement in mental health can be attributed to the balanced blood sugar levels achieved by avoiding excessive added sugars, which can lead to spikes followed by crashes that affect mood.
As individuals distance themselves from high-sugar diets, they may also gain a healthier relationship with food and eating. This process encourages mindfulness and helps combat urges stemming from cravings. Over time, people can learn to enjoy their meals and snacks without the overpowering influence of added sugars, leading to greater satisfaction.
Social and Environmental Influences on Sugar Consumption
The environment in which we live significantly impacts our dietary choices, including sugar consumption. Accessibility to sugary foods is often tied to marketing practices that associate happiness with sweetness. Children’s products are particularly targeted, with brightly colored packages and cartoon characters that make sugary snacks appealing. This societal norm can create a culture where sugar consumption is normalized, making it harder for individuals to reduce their intake.
Efforts to combat these influences can include increasing public awareness about the health effects of sugar and advocating for policy changes that promote healthier eating habits. Schools and communities that integrate healthy eating initiatives can help shift societal norms towards better nutrition, supporting individuals in making informed choices about sugar consumption.
Finding Alternatives to Sugar for Wellness
With the growing awareness of sugar’s health implications, many individuals are exploring alternatives to satisfy their sweet tooth while maintaining their health. Options such as natural sweeteners like honey or maple syrup, along with sugar substitutes like stevia or monk fruit, offer a way to enjoy sweetness without the same health drawbacks as traditional sugar.
Moreover, incorporating fruits as a natural source of sweetness in recipes can provide added nutritional benefits. Emphasizing whole, minimally processed foods not only reduces sugar consumption but also enhances overall health, supporting long-term wellness goals. By focusing on natural alternatives, individuals can enjoy their favorite flavors while making healthier dietary choices.
Frequently Asked Questions
Is sugar addictive like alcohol or nicotine?
While sugar is not classified as an addictive substance like alcohol or nicotine, it can induce cravings and compulsive eating behavior. The health effects of sugar can mimic some withdrawal symptoms, making it a complex issue to navigate.
What are the health effects of sugar addiction?
Excessive sugar consumption can lead to various health issues, such as obesity, diabetes, and heart disease. It can also cause withdrawal-like symptoms when reduced, highlighting the addictive qualities of sugar in processed foods.
How do sugar cravings compare to other addictive substances?
Sugar cravings can be strong, akin to those associated with addictive substances. However, while withdrawal symptoms may occur when cutting back on sugar, they are generally less severe than those related to substances like alcohol or nicotine.
Can processed foods increase sugar cravings?
Yes, processed foods often contain high levels of added sugars, unhealthy fats, and sodium, which can amplify sugar cravings. This can lead to habitual sugar consumption, making it harder to reduce intake.
How can one manage sugar consumption to avoid addiction?
To manage sugar consumption, gradually reduce the amount of added sugar in your diet, read food labels carefully, and prioritize whole foods. This approach can minimize cravings and help maintain a balanced diet.
Is a small amount of sugar necessary in our diet?
Yes, an appropriate amount of sugar can enhance flavor and provide energy. Unlike addictive substances, sugar is present in many natural foods, including fruits and whole grains, which makes it essential for a balanced diet.
What is the recommended daily limit for sugar consumption?
The American Heart Association recommends that men consume no more than 9 teaspoons and women no more than 6 teaspoons of added sugar per day. Keeping within these limits can help avoid potential health issues associated with excessive sugar consumption.
| Key Points | Details |
|---|---|
| Is Sugar Addictive? | The debate on whether sugar is addictive is ongoing. Sugar can create cravings similar to addictive substances, but it isn’t classified as addictive by clinical standards. |
| Withdrawal Symptoms | When people stop consuming high-sugar, ultra-processed foods, they may experience withdrawal-like symptoms such as headaches and anxiety. However, these are milder compared to substances like alcohol or nicotine. |
| Role of Sugar in Diet | Sugar is necessary for flavor and can be part of a balanced diet when consumed in moderation. It is found naturally in many healthy foods like fruits and whole grains. |
| Recommended Intake | The American Heart Association recommends limiting added sugar intake to 9 teaspoons for men, 6 for women, and less for children. The average American consumes nearly 20 teaspoons daily. |
| Moderation is Key | Moderate consumption of sugar doesn’t typically lead to major health problems, but awareness of sugar intake is essential. Gradual reduction is recommended rather than going ‘cold turkey’. |
Summary
Is sugar addictive? The answer is nuanced; while sugar can lead to cravings and compulsive eating behaviors, it is not officially classified as an addictive substance like alcohol or nicotine. Sugar plays a significant role in our diet and should be consumed in moderation. Understanding the balance of sugar intake is crucial for health, highlighting the importance of being mindful about the sources of sugar in our foods.