Neurological Basis of Social Connection Revealed in New Study
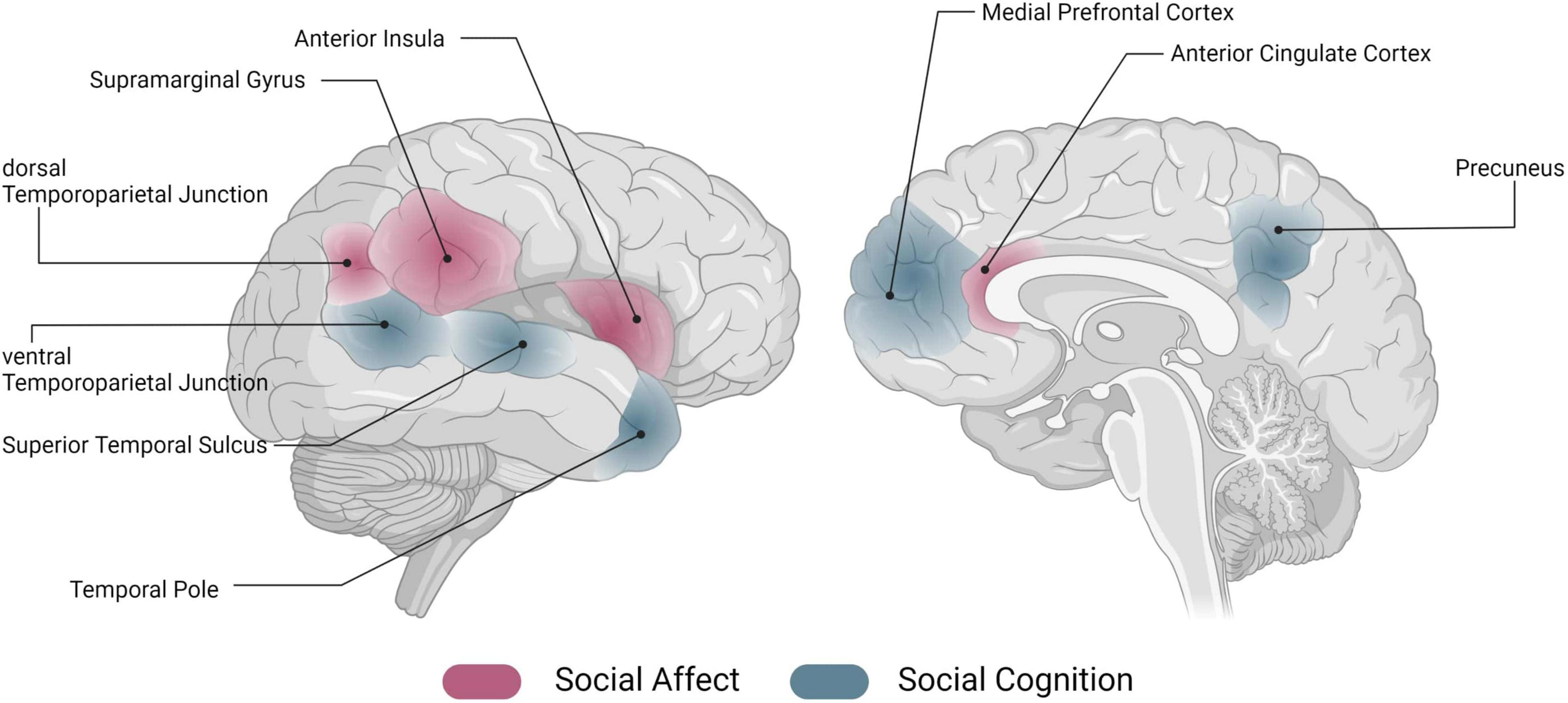
The neurological basis of social connection is an intriguing field of study, shedding light on why humans have an innate need for social interaction comparable to basic needs like food and water. Research has revealed that the brain’s mechanisms, particularly in regions such as the hypothalamus, control how we seek out companionship and respond to social isolation effects. As highlighted by recent neurological studies, interpersonal relationships are crucial not only for emotional well-being but also for mental health and social needs. Furthermore, understanding how these connections function at a biological level can provide insights into the damaging effects of loneliness. This fascinating exploration into the brain’s architecture enhances our appreciation of social bonds, vital for nurturing healthy lives.
Exploring the neurological foundations of human connectivity unveils the deeper reasons behind our social instincts. The interaction among various brain circuits illustrates how essential companionship is, much like our physiological requirements for nourishment and hydration. This research emphasizes the crucial importance of social engagement in maintaining mental well-being and the implications of social isolation on psychological health. By understanding how our brains activate during social interactions, we begin to see the pivotal role these connections play in our lives. Ultimately, these findings could reshape how we approach the complexities of social relationships and their impact on our overall health.
The Neurological Basis of Social Connection
Research increasingly highlights social connection as a fundamental aspect of human health, not merely an emotional luxury. Studies conducted by Liu and his team reveal the intricate neurological underpinnings that drive social behaviors, identifying specific neurons in the hypothalamus that become active during periods of social deprivation. This understanding repositions the need for social interaction alongside basic biological needs such as food and water, showcasing how critical social engagement is for maintaining mental well-being.
Furthermore, the concept that the desire for social interaction may stem from a drive to avoid negative states, akin to hunger and thirst, opens a new avenue of inquiry into the neuroscience of social connection. By understanding these mechanisms, researchers can begin to untangle the complexities behind social isolation effects and how prolonged absence from social environments can deteriorate both mental and emotional health. This neurological insight serves as a groundwork for further studies on the importance of fostering social networks and combating loneliness.
Social Isolation Effects on Mental Health
The implications of social isolation on mental health are profound and multifaceted. Individuals experiencing prolonged periods of solitude often report heightened feelings of anxiety and depression, which can lead to more severe mental health issues over time. Research has shown that the brain responds to social deprivation in similar ways it responds to physical hunger, indicating that the need for social interaction is not just a psychological craving but also a biological imperative.
When social connections are lost, the hypothalamic circuit’s function associated with social needs becomes disrupted, leading to detrimental effects on both mood and cognitive function. Such findings underscore the vital role communal interactions play in mental health and highlight the urgent need to address social isolation as a critical public health issue, especially in contemporary times where digital interactions often replace face-to-face engagements.
Importance of Social Interaction in Human Development
Social interaction is essential for healthy human development across all life stages. From infancy to old age, building relationships has a critical influence on emotional and psychological growth. Infants thrive on interactions with caregivers, which establish the foundation for secure attachment and social learning. As individuals progress into adulthood, these interactions foster resilience, reduce stress, and encourage positive mental health outcomes.
In fact, studies indicate that socially integrated individuals experience better overall health, lower rates of anxiety, and improved emotional regulation compared to those who are socially isolated. By understanding the biological and psychological foundations of social behavior, efforts can be made to encourage meaningful connections, thereby enhancing the quality of life for individuals and communities alike.
The Role of Touch in Strengthening Social Bonds
Touch is a significant yet often overlooked aspect of social interaction that profoundly affects human connection. Liu’s studies emphasize the importance of tactile stimulation in fulfilling social needs, pointing out that mere visual or auditory cues are insufficient for complete social engagement. The mice experiments demonstrated a marked preference for physical comfort and contact, revealing how touch can alleviate feelings of isolation and promote a sense of belonging.
For humans, physical touch manifests in various forms—hugs, handshakes, and casual touches during conversations—all of which reinforce social bonds and foster trust. As society moves towards more digital communication platforms, recognizing the loss of these tactile interactions is essential. Acknowledging touch’s significance could lead to strategies aimed at enriching social engagement in increasingly isolated environments, ultimately benefiting mental health.
Hypothalamic Circuit Function: A Key Player in Social Needs
The hypothalamus plays a central role in regulating many of our body’s essential functions—hunger, thirst, and even social interaction. Recent neurological studies have illustrated that this brain region not only governs physiological needs but also encodes the desire for social contact. Liu’s research specifically focused on how the hypothalamic circuit adjusts based on social experiences, demonstrating its dual function in balancing both physiological and social homeostasis.
Disruption in hypothalamic functions can lead to insufficient social engagement, illustrating the importance of maintaining healthy social ties for overall well-being. By investigating how these neural circuits operate and interact with various social stimuli, researchers can better understand the complexities of social needs and their influence on mental health, paving the way for potential therapeutic approaches to combat social disengagement.
Connecting Social Behavior to Biological Imperatives
Understanding social behavior through the lens of biological needs shifts the discourse around mental health and well-being. As established by Liu and Dulac, social connection is not just pivotal for emotional support but is fundamentally linked to our biological survival mechanisms. The brain’s response to social isolation showcases that our social networks are as crucial as physical needs like food and water, compelling us to reevaluate our priorities in building and maintaining relationships.
This redefined perspective of social connectivity highlights why fostering inclusive environments that promote social interactions is so crucial. By articulating the biological imperatives behind social needs, public health initiatives can better target interventions aiming to alleviate social isolation effects, ultimately leading to healthier and more resilient populations.
Navigating Loneliness in a Digital Age
In an era characterized by rapid technological advancements, the way we connect has drastically changed, often sidelining face-to-face interaction. The rise of social media has created a paradox where individuals can feel more isolated despite being virtually connected. Liu’s insights into the neurological implications of social isolation highlight the pressing need to seek authentic connections beyond the digital realm, emphasizing the value of direct human contact.
Moreover, understanding the neuroscience behind our social needs can inform public health strategies aimed at combating feelings of loneliness prevalent in a screen-dominated world. Encouraging community activities and relationship-building initiatives can provide opportunities for genuine interaction, reinforcing the importance of physical presence in nurturing our psychological well-being.
Insightful Approaches to Mental Health and Social Needs
The emerging understanding of the interplay between social needs and mental health opens up new avenues for treatment and support. As research progresses, mental health professionals are called to incorporate findings about the neurological basis of social connection into therapeutic practices. Addressing social isolation and fostering community involvement might become part of holistic treatment plans aimed at enhancing emotional resilience.
By prioritizing social interactions as a vital component of mental health care, therapists and practitioners may mitigate the severity of mental illnesses tied to social isolation, providing patients with tools to engage meaningfully in their communities. Collaborative approaches that intertwine neuroscience with mental health practices can lead to innovative support systems that champion the importance of social connectivity in healing and recovery.
Future Implications for Social Science and Neurobiology
The future of social science and neurobiology is at a pivotal junction, with emerging research shedding light on complex interactions between brain function, social behavior, and health. The insights gleaned from studies like those conducted by Liu and Dulac demonstrate the necessity for interdisciplinary approaches that meld neuroscience with psychological and sociological frameworks. This synthesis could inform policy-making and public initiatives aimed at reducing social isolation and enhancing community relationships.
As researchers continue to uncover the neurological foundations of social connection, opportunities arise not only for academic inquiry but also for practical applications in mental health, education, and community development. Engaging with the biological basis of our social instincts stands to transform our understanding of interpersonal relationships, ultimately enriching lives through deeper human connection.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is the neurological basis of social connection and its effects on mental health?
The neurological basis of social connection involves understanding how the brain encodes the need for social interaction through specific neural circuits, notably in the hypothalamus. Research indicates that social connections are as vital for mental health as basic needs like food and water, with studies showing that social isolation can lead to negative psychological outcomes. The brain’s response to social isolation and the mechanisms that drive the need for social interaction highlight its importance in maintaining mental well-being.
How does social isolation affect neurological function?
Social isolation has significant effects on neurological function as evidenced by studies that demonstrate changes in brain activity during periods of solitude. For example, research shows that when social contact is restricted, specific neurons in the hypothalamus activate, reflecting the brain’s response to the deprivation of social interaction. Consequently, prolonged social isolation can lead to negative changes in behavior and mental health, including a decrease in social interest.
What are the physiological needs compared to the need for social interactions?
Physiological needs such as hunger, thirst, and sleep are similarly encoded in the brain as social interactions, indicating that both are fundamental requirements for health. Recent neurological studies, including those from the Dulac Lab, highlight that the brain’s mechanisms, particularly in the hypothalamic circuits, govern not only basic physiological needs but also the social needs that contribute to our overall mental health.
Why is the importance of social interaction highlighted in neurological studies?
The importance of social interaction is highlighted in neurological studies due to its profound impact on mental health. Research indicates that social interactions activate specific brain circuits that are crucial for psychological well-being. Understanding these mechanisms allows for better insights into how social behaviors influence mental health and how deficits in social interaction can lead to disorders, thereby prompting a need for further investigation in this field.
What are the implications of neurological research on social needs for human behavior?
Neurological research on social needs has significant implications for understanding human behavior. By exploring the brain’s response to social isolation and the intricacies of social bonding, these studies provide insight into the biological and psychological foundations of relationships. This knowledge may aid in addressing mental health issues linked to social deficits, highlighting the necessity for social interaction similar to other vital human needs.
| Aspect | Details |
|---|---|
| Study Focus | Investigating the neurological basis of social connection. |
| Key Finding | Social connection is as crucial as food and water, with neurological systems governing the human need for interaction. |
| Research Methodology | Isolating mice to observe neural reactions during social deprivation and reunion phases. |
| Significant Insight | The desire for social interaction may be more about avoiding negative feelings (similar to hunger) rather than purely seeking positive experiences. |
| Neural Activity | Identified neurons in the hypothalamus that activate during social seeking and satiety phases. |
| Impact of Isolation | Prolonged isolation leads to aversion to social interaction. |
| Touch’s Importance | Physical touch is vital for social satisfaction, with preferences shown for tactile stimuli post-isolation. |
| Broader Implications | Research aims to understand the biological and psychological needs for socializing, with relevance to mental health. |
Summary
The neurological basis of social connection is critical in understanding human behavior and mental health. Recent research has revealed that social interactions are fundamental needs, much like hunger and thirst. This study highlights the intricate neural mechanisms involved, linking social behavior to our physiological urges. By recognizing these connections, we can appreciate the vital role of socialization in maintaining psychological well-being and develop better strategies to address mental health issues.