CRISPR gene editing is revolutionizing the landscape of modern medicine, offering unprecedented potential to alter genetic codes with precision. The marvel of CRISPR technology opens doors to effective treatments, such as curing sickle cell anemia, yet it also thrusts forward a plethora of ethical dilemmas regarding gene editing ethics. As highlighted by experts like Neal Baer, the implications of manipulating genes extend beyond mere medical benefits—they prompt critical conversations about health equity and access to treatments. With such powerful tools at our disposal, we face significant controversies surrounding gene therapy, especially concerning who decides what constitutes a desirable trait. The balance between transformative healthcare and responsible implementation remains a pivotal focus for the future of CRISPR gene editing.
Utilizing cutting-edge genetic modification techniques, CRISPR technology offers scientists an innovative approach to address hereditary diseases like sickle cell disease. This genetic editing framework is transforming the way we think about illness, opening discussions about gene therapy debates that question the morality of altering human genetics. Such advancements compel us to examine the social ramifications, particularly in regard to health disparities and the ethical considerations surrounding the rights to modify one’s own genetic material. As we embrace this potential for curing genetic disorders, we must also grapple with the broader implications of our choices, including the influence of socio-economic factors on health outcomes. In navigating these pressing topics, we highlight the importance of fostering a dialogue that encompasses both the scientific possibilities and the societal responsibilities that come with CRISPR gene editing.
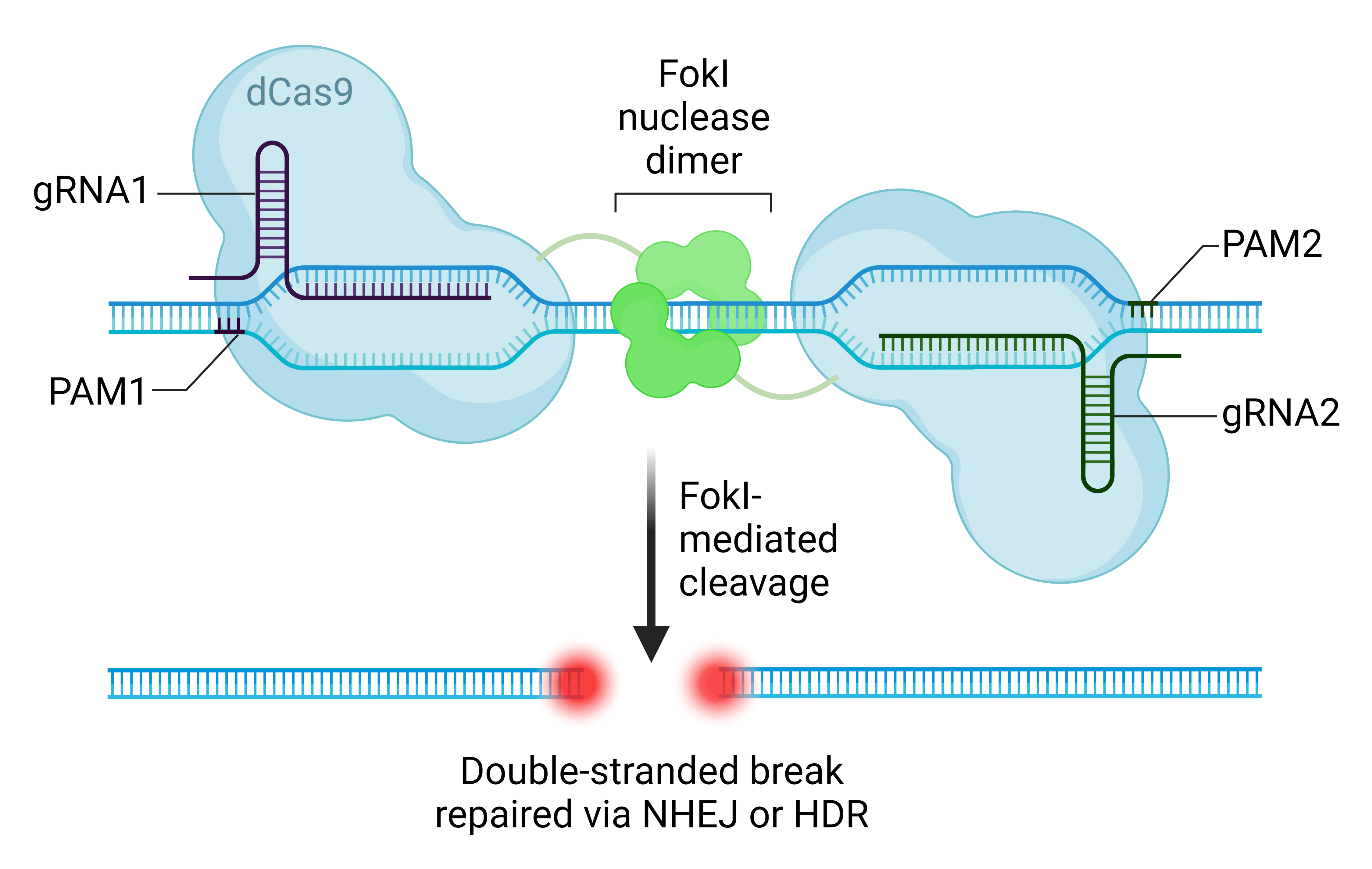
Understanding CRISPR Gene Editing: A Revolution in Medicine
CRISPR gene editing has emerged as one of the most groundbreaking innovations in biotechnology. This precise and efficient method allows scientists to alter DNA sequences and modify gene function, enabling potential cures for previously untreatable diseases. In the context of sickle cell disease, CRISPR technology holds the promise of curing patients by directly targeting the defective genes responsible for this debilitating condition. Through the correction of these genetic mutations, individuals who were once afflicted with symptoms like severe pain and repeated medical emergencies may find relief and enjoy a better quality of life.
However, with great power comes great responsibility. While the potential benefits of CRISPR are immense, it simultaneously raises significant ethical questions. For instance, the ability to edit human genes opens the door to modifying traits that extend beyond health, such as physical appearance or intelligence. This potential for ‘designer babies’ necessitates rigorous ethical discussions among scientists, ethicists, and society at large. By navigating the implications surrounding CRISPR gene editing, we can ensure that its applications align not only with medical advancements but also with our collective moral values.
The Ethical Implications of Gene Editing Technologies
The ethics of gene editing, particularly in the context of CRISPR, is a hotly debated topic among health professionals and bioethicists alike. The ability to edit genes for conditions like sickle cell disease raises questions about whether it is acceptable to change fundamental aspects of human biology. Some argue that attempting to eliminate diseases is a step towards a healthier future, promoting health equity and access to vital medical advancements. However, there are significant concerns about who gets to decide what constitutes a ‘disease’ worthy of eradication, especially in the case of conditions that do not severely impact quality of life.
Furthermore, the financial aspects of gene therapy bring additional ethical considerations to the fore. For instance, with treatments like the sickle cell cure costing exorbitant amounts—around $2.2 million per patient—access to such life-altering interventions becomes a privilege limited to the wealthy. This inequity presents a troubling reality for health equity advocates, who argue that all patients, regardless of their socio-economic status, should have access to emerging therapies. Thus, ongoing dialogue about the frameworks and regulations governing gene editing technologies is crucial to ensure that innovation does not outpace ethical accountability.
Exploring Sickle Cell Treatment: The Role of CRISPR
Sickle cell disease, a hereditary blood disorder that affects thousands worldwide, has long been a challenge for medical professionals. The advent of CRISPR technology presents a beacon of hope in the quest for effective treatments. By using CRISPR, clinicians can target and edit the specific genes that cause sickle cell anemia, potentially transforming how this condition is managed. The excitement surrounding these advancements is palpable, as researchers observe promising results in trials, showcasing significant improvements in patients’ conditions and their overall quality of life.
Nevertheless, these advancements come with a caveat. Though the technology is revolutionary, ethical dilemmas emerge regarding genetic modifications. Should gene editing be utilized solely for conditions like sickle cell disease, or can it extend to more subjective genetic changes? Moreover, as we continue to explore the efficacy of CRISPR in treating this disease, it is critical to address the implications of access and affordability. Ensuring that breakthroughs in gene therapy are accessible to all individuals with sickle cell disease must be a foremost priority, to eliminate disparities in treatment across different populations.
Health Equity and the Future of Gene Editing
The introduction of CRISPR gene editing technology has the potential to redefine health equity by addressing the disparities seen in the treatment of genetic conditions, including sickle cell disease. The hope is that as CRISPR becomes more widely available, it will not only provide cures for genetic disorders but also level the playing field for those who have historically faced systemic barriers to healthcare. Advocates for health equity argue that biotechnology should work towards dismantling these barriers, ensuring equitable access to cutting-edge treatments regardless of socio-economic background.
Furthermore, dialogue surrounding health equity must engage with the ethical dimensions of these innovations. As the costs of gene editing therapies remain high, the question becomes who will benefit from these advancements. Ensuring that marginalized communities are not left behind in the wake of new medical breakthroughs requires proactive measures from healthcare providers and policymakers. By creating frameworks that promote equitable access to CRISPR and similar technologies, we can harness the power of gene editing for the greater good, fostering a healthier society for all.
Gene Therapy Controversies: Navigating New Frontiers
As gene editing technologies like CRISPR grow more sophisticated, they also spark a myriad of controversies that must be carefully navigated. One of the foremost debates revolves around the ethical implications of germline editing, where changes made to an embryo can be passed down to future generations. While proponents argue this could eliminate hereditary diseases, critics warn of unintended consequences and long-term impacts on genetic diversity. The question of how far we should go in modifying human genetics remains contentious, highlighting the need for stringent regulations and ethical guidelines.
Additionally, the accessibility of gene therapies raises ethical concerns. Although advances like CRISPR offer revolutionary potential to treat diseases, the exorbitant costs associated with such treatments pose a significant barrier for many individuals and communities. This disparity risks exacerbating existing health inequalities, where only the affluent can access life-saving modifications while low-income populations remain deprived of these benefits. As the gene editing landscape evolves, a concerted effort is needed to ensure that ethical considerations are at the forefront, safeguarding against the commodification of human health.
Navigating the Future: Ethical Considerations in Gene Editing
The rapid advancement of gene editing technologies opens up a multitude of possibilities, but it also compels society to confront complex ethical dilemmas. As we explore the capabilities of CRISPR and other gene-editing tools, we must consider the broader implications of manipulating the human genome. Ethical questions arise regarding consent, especially in cases involving germline editing where future generations may be affected by decisions made today. Thoughtful discussions and comprehensive regulatory frameworks are essential in guiding the responsible use of gene editing technology.
Moreover, transparency and public engagement are critical in shaping the future of gene editing. Scientists, ethicists, and policymakers must engage in open dialogues with communities to foster understanding and address public concerns about gene modification. Striking a balance between innovation and ethical integrity will be pivotal in harnessing the benefits of CRISPR while mitigating its risks. By prioritizing ethical considerations alongside scientific advancement, we can ensure that gene editing contributes positively to society and embodies the principles of justice and equity.
What Drives the Demand for CRISPR in Medicine?
The increasing demand for CRISPR technology in the medical field underscores the urgent need for effective treatments for genetic disorders. With an estimated 100,000 individuals suffering from sickle cell disease in the U.S. alone, the call for innovative solutions is stronger than ever. As CRISPR emerges as a feasible option for gene editing, many healthcare professionals and patients are advocating for its implementation, driven by hopes of finding cures rather than merely managing symptoms. This shift towards an innovative treatment paradigm highlights a growing impatience with the prevailing healthcare models that often rely on inadequate responses to chronic diseases.
Additionally, as public awareness of genetic diseases and their societal implications rises, so does the demand for groundbreaking therapies like CRISPR. Patients and advocacy groups are increasingly influencing healthcare conversations, pushing for the prioritization of gene therapies that can directly tackle genetic issues at their source. This grassroots momentum signals a transformative change in how society perceives health challenges and the potential of biomedical innovations. By stimulating interest and investment in CRISPR technology, we pave the way for potential breakthroughs that could redefine treatment paradigms across various genetic disorders.
The Promise of CRISPR Beyond Disease Treatment
While the primary focus of CRISPR gene editing has been on the treatment of genetic disorders, its potential applications extend far beyond healthcare. For instance, this technology could play a significant role in environmental and agricultural advancements. Scientists are exploring the use of CRISPR to create genetically modified crops that can withstand pests, diseases, and climate change effects, ultimately contributing to food security. By applying gene editing to enhance agricultural productivity sustainably, CRISPR could help address global hunger challenges and support environmental conservation efforts.
However, the same ethical considerations that apply to medical applications of CRISPR also extend to its use in agriculture and the environment. As we unlock the potential of these technologies, it is vital to engage in dialogues about the ecological implications and the societal ramifications of altering ecosystems. Ensuring that CRISPR’s application in agriculture is done responsibly and equitably is paramount to avoid unintended consequences on biodiversity. By considering the broader impacts of gene editing beyond human health, we can maximize its benefits while safeguarding ethical standards.
Public Perception of Gene Editing Technologies
The public perception of CRISPR and broader gene editing technologies is a significant factor influencing their acceptance and integration into medical practice. While many individuals view these advancements as promising solutions to chronic diseases, there is also a degree of apprehension surrounding the implications of genetic manipulation. The science fiction-esque notions of ‘designer babies’ and ethical misalignments provoke concerns about where to draw the line in editing human traits. Public education and discussion are essential to demystify these technologies and promote informed viewpoints.
Additionally, transparency in scientific research and its applications can foster trust among communities potentially affected by gene editing. As scientists and bioethicists work to navigate the complex ethical landscape, engaging with the public can help demystify the technology and address concerns about its safety, efficacy, and implications. By creating an informed dialogue, we can anchor CRISPR’s reputation within society and support its responsible evolution, ensuring that advancements align with public interest and ethical responsibility.
Frequently Asked Questions
What ethical concerns are associated with CRISPR gene editing?
CRISPR gene editing raises significant ethical concerns, particularly regarding the implications of altering human genes. Key issues include the morality of modifying traits that are compatible with life, the potential for eugenics, and the consequences of creating inequalities in access to these technologies. Experts like Neal Baer emphasize the need for discussions on who has the authority to make such decisions, as well as the importance of health equity.
How could CRISPR technology impact treatments for sickle cell disease?
CRISPR technology offers a promising avenue for treating sickle cell disease by allowing scientists to edit the genes responsible for the condition. This could potentially lead to cures that eliminate the disease at a genetic level. However, concerns about affordability, access, and ethical considerations surrounding gene editing must be addressed to ensure that all patients benefit from these advancements.
What are the implications of gene therapy controversies in CRISPR research?
Gene therapy controversies in CRISPR research revolve around the ethical use of gene editing on human embryos, potential long-term impacts on the human gene pool, and debates over informed consent. These controversies highlight the need for a robust ethical framework to navigate the complexities of gene editing technology and its applications.
How can CRISPR gene editing contribute to health equity?
CRISPR gene editing has the potential to significantly improve health equity by offering treatments that could alleviate genetic diseases, such as sickle cell anemia. However, achieving health equity requires addressing access to these therapies, ensuring that marginalized communities benefit from advancements in CRISPR technology without exacerbating existing inequalities in healthcare.
What role do ethical considerations play in the future of CRISPR gene editing applications?
Ethical considerations are crucial in shaping the future of CRISPR gene editing applications. Discussions around the appropriateness of gene modification for non-life-threatening conditions, parental decision-making about genetic attributes, and regulatory oversight are essential. As technology evolves, ethical frameworks must keep pace to guide responsible use and minimize potential misuse of CRISPR technology.
| Topic | Details |
|---|---|
| CRISPR Gene Editing | A revolutionary technology that allows for precise editing of genes to treat genetic disorders. |
| Ethical Dilemmas | Debate over the morality of changing human attributes and potential unintended consequences. |
| Examples of Application | Successful treatments for conditions like sickle cell anemia; concerns about editing genes related to non-life-threatening syndromes. |
| Health Equity | High costs of gene therapies raise questions about accessibility and fairness in healthcare. |
| Global Oversight | Concerns about the lack of regulation and monitoring in various countries regarding gene editing practices. |
Summary
CRISPR gene editing is a groundbreaking technology that presents both vast potentials and ethical challenges. As scientists explore the capacity to alter genetic makeup for the betterment of health, the question arises about the moral implications of such power. While CRISPR offers hope for curing devastating diseases like sickle cell anemia, it prompts a reevaluation of what it means to be human, the equity of healthcare access, and the responsibilities attached to genetic interventions. Engaging in dialogue about these issues is crucial as we navigate the future of gene editing.